
Shrimp breeding for low-protein or vegetable-protein diets unnecessary
Most shrimp cultured today are fed diets with greater than 30 percent protein, with much of this protein obtained from fishmeal.
Low dissolved oxygen is associated with stressful conditions for shrimp. Liquid oxygen injection systems are a potential solution.

Most shrimp cultured today are fed diets with greater than 30 percent protein, with much of this protein obtained from fishmeal.
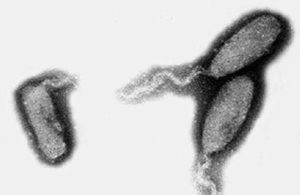
Australia’s prawn industry has encountered its first scare over white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) following positive test results in the northern territories.

Phospholipids and cholesterol are essential lipids for shrimp yet knowledge of dietary requirements during the juvenile stage is still limited.

Aerated microbial reuse systems recycle nutrients in the form of organic detritus, which consists of aggregates of organic particles coated with a film of bacteria.

Several studies now suggest the color of indoor aquaculture tanks should also be considered for improved animal health and performance in indoor systems.

In marine fish hatcheries, a mesocosm is a tank or pond in which a natural phytoplankton or zooplankton bloom is developed prior to stocking yolk-sac larvae.

Probiotic bacteria may inhibit the migration of viruses among cultured fishes and strengthen their immune systems.
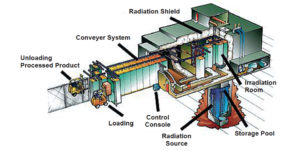
Irradiation is exposing food to controlled levels of ionizing radiation, killing microorganisms without changing texture, flavor or nutritional value.

Results of this trial show it's possible to reestablish L. vannamei production in a WSSV-infected region, even with a continued viral source on the same farm.
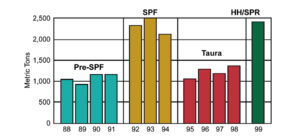
Recent successes have proven that breeding shrimp for fast growth and virus resistance is both feasible and highly effective.

As shrimp hatcheries continue replacing wild postlarvae, it is important to examine other areas of their operation that relate to the environment.

Libraries have been produced from Pacific white shrimp containing many thousands of microsatellites, a source of potential markers for use in diverse applications.

Prophylaxis and quarantine are mandatory steps prior to maturation, spawning, larval rearing and fingerling production in a marine fish hatchery.

Excess nutrients from poor feeding regimes result in accumulated sludge on the bottoms of shrimp ponds, harming the environment and animal health.

The use of intensive raceway nursery systems to produce juvenile shrimp under biosecure conditions is an important WSSV management tool.