
Bacterial pathogens in biofilms pose health risks in recirculating systems
Recirculating aquaculture presents an increased potential for pathogenic bacteria to become established in the system through the formation of biofilms.
In combination with the aquaculture value chain multi-residue detection systems can assure that safe and wholesome products reach consumers.

Recirculating aquaculture presents an increased potential for pathogenic bacteria to become established in the system through the formation of biofilms.

The administration of any pharmaceutically active chemical to a food-producing animal results in the occurrence of antibiotic residues in food.

Shrimp health management focuses on disease prevention through good nutrition, sound pond management, and stress reduction rather than disease treatment.

An approach like HACCP, which integrates risk assessment, management and communication is necessary to minimize unintended consequences.

Since microbiological analyses do not provide a desired degree of reliability, chemical tests have been proposed for farmed fish quality assurance.

The detection of the antibiotic chloramphenicol in shrimp exported to Europe from Asian countries brought about a flood of reactions.

During the 1970s and 1980s, Ecuador's shrimp industry relied almost entirely on wild postlarvae but has since developed large hatcheries.

The Nicaragua Small Shrimp Producer Assistance Program built a closed, zero water-exchange shrimp production system to demonstrate the concepts and practices.
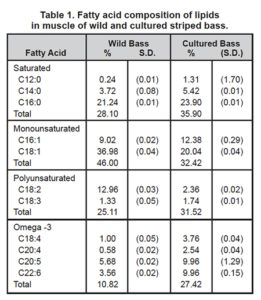
Studies comparing the differences between farmed and wild fish lipid profiles have been conducted, but there is no standard format for reporting.

Sexual growth dimorphism occurs in cultured aquatic species like tilapia, catfish and salmon, and has also been reported for cultured crustaceans.

Catfish feeds used in trials at LSU were formulated to possess an amino acid balance similar to that of the channel catfish body.

Commercial experience and research have demonstrated that phosphates can enhance sensory quality and increase consumer appeal for shrimp. Through over 10 years of research with shrimp from around the world, the Aquatic Food Products Lab at the University of Florida in Gainesville, Florida, USA has shown that consumers prefer shrimp properly treated with phosphates. However, processors must have a clear understanding that misuse of these ingredients can result in poor appearance, poor texture, and consumer rejection.

EU markets have special requirements for head-on shrimp. Organoleptic criteria are evaluated, including firmness of shell and head, malformations and color.
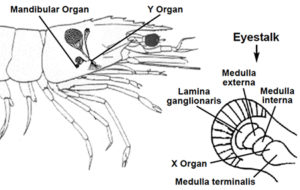
In most decapod crustaceans the physiological processes of metamorphosis, molting and reproduction are inextricably linked and controlled by hormones.

Rotifers are a dominant zooplankton that are a preferred prey for larval fish and one of the live feeds most often used by fish culturists.