
Trans-fatty acids health concerns, labeling requirements
FDA’s regulatory definition for trans-fatty acids is all unsaturated fatty acids that contain one or more isolated double bonds in a trans configuration.
Shrimp farming in Belize, Central America, was hard hit by Taura Syndrome Virus (TSV, now known as TSV serotype A) in 1996 and a re-emergence in 2002.

FDA’s regulatory definition for trans-fatty acids is all unsaturated fatty acids that contain one or more isolated double bonds in a trans configuration.

Both microsatellite and AFLP marker analyses can provide adequate screening of genetic diversity in tilapia stocks at a low cost.

Determining the digestibility of protein and other nutrients in feed ingredients is an important step in the formulation of balanced feed.

Slurry ice is widely adopted in major fisheries around the world, where ice companies work with fishermen and seafood processors to develop better methods of preservation.

Specific pathogen-free status depends on the presence or absence of specific pathogens. This status depends on the level of biosecurity for the shrimp.

Dried artemia biomass and other crustacean meals could be cost-efficient alternatives for shrimp hatcheries as the only feed used to rear shrimp postlarvae.

Zero tolerance for chloramphenicol residue in food by the European Community indicates that chloramphenicol risks are regarded as real by European regulators.

U.S. news media, doctors and even dietitians are warning patients that methylmercury in fish can harm them, their children and their unborn children.

Many production aspects in shrimp culture are related to the molt stage, such as mating in closed-thelycum species, market value and eyestalk ablation.

Studies show that dietary arachidonic acid improves fish survival and growth if offered together with suitable levels of the other essential fatty acids.

Dietary gossypol from cotton seeds, if present in large amounts in a diet, causes unfavorable physiological effects in monogastric animals including fish.

Wild and cultured fish around the world are commonly affected by piscine mycobacteriosis, infections of which often manifest as acute or chronic diseases.

Since the first pioneer shrimp farm was established in the area in 1997, desert shrimp farming in Arizona, USA, has expanded rapidly.
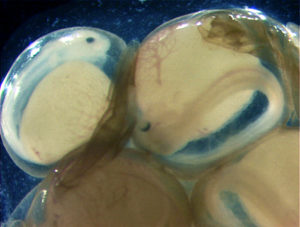
Without hydrogen peroxide treatments, pathogens like fungi and bacteria can overtake the egg mass and significantly reduce channel catfish embryo survival.

The development of land-based, hyperintensive farming systems for fish and shellfish production could quickly expand in industrialized countries.