
Rearing diets for winter flounder optimize weaning success in hatchery, wild
In hatchery feeding trials, winter flounder juveniles reared on white worms grew the most, while pellet-reared fish had the lowest growth and survival.
To alleviate problems associated with conducting research on fish of unknown and likely diverse genetic backgrounds, a collaborative project has been established to produce a stock of rainbow trout with a defined genetic background for use in fish nutrition research.

In hatchery feeding trials, winter flounder juveniles reared on white worms grew the most, while pellet-reared fish had the lowest growth and survival.

USDA and partners are developing channel catfish that exhibit superior growth, fillet yield and resistance to enteric septicemia. Although ongoing research continues to select the USDA lines for better performance, studies comparing the strains have been inconclusive.

New Zealand’s National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research has established broodstock research for several emerging species to provide genetically diverse, domesticated stocks for aquaculture industry expansion.

In general, benefits from genetic increases in growth rate result from better farm environments. Breeding programs should focus selection on genes expressed favorably in the environment that most affect farm profit.

Regular surveillance of culture stocks can both evaluate current animal health and limit future disease problems by detecting pathogens and allowing intervention before disease outbreaks occur.

Measures can be taken to lessen or avoid the effects of disease outbreaks. Preventive measures are the most effective, although various vaccines can help limit the impacts of diseases and further decrease reliance on antibiotics.

The main reason for recent declines in blue mussel yields in the Netherlands was lower availability of mussel seed. Mild winters have increased the number of predators, which can decimate mussel stocks.
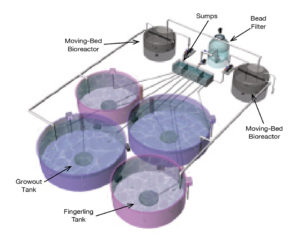
A boutique design project validated a land-based, recirculating production system capable of producing 50 metric tons of spotted sea trout per year.

The growth and survival of red tilapia fry were not significantly affected by different photoperiods in three 30-day experiments. Results suggested that it is not necessary to maintain constant lighting or a constant light/dark circadian scheme.

Induced triploidy could theoretically improve the survival of cultured hard clams because triploids divert energy from reproduction to somatic growth, resulting in larger and potentially hardier clams than diploids.

Researchers found juvenile queen conch fed diets containing added macroalgae had higher survival than a control given catfish feed only.

With high value in U.S. markets and its overfished status, red porgy appears to be a viable candidate for aquaculture in North America.

To avoid or control the impacts of disease, consistent observation and sampling of animals are essential. Sample size should be dictated by the goal of the sampling.

Ozone is a strong oxidizing agent that effectively removes colors, odors and turbidity from water, and kills bacteria, viruses and other microorganisms.
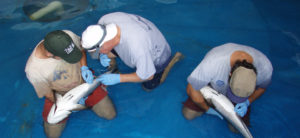
Selective-breeding coupled with advances in maturation systems, nutrition and management led to natural cobia spawnings at the University of Miami Experimental Hatchery.