
Within-family selection enhances shrimp growth
A study in Brazil found that the growth superiority brought about by within-family selection of tested shrimp transmitted to the next generation of animals.
Published information on the effects of including organic acids and their salts at low concentrations in aquafeeds varies according to fish species and age, as well as the types and levels of organic acids and salts used.

A study in Brazil found that the growth superiority brought about by within-family selection of tested shrimp transmitted to the next generation of animals.
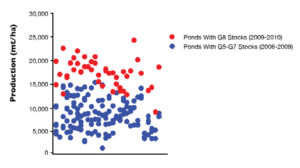
Traditionally, Australian farmers relied on wild broodstock to source black tiger shrimp larvae, but substantial progress has been made in the domestication and selective breeding of Australian P. monodon.

The basic premise of refrigeration is to move heat from a colder heat source to a warmer heat sink. Common pitfalls for refrigeration in aquaculture are a lack of water flow, inadequate evaporator capacity and evaporator freezing.

In research involving white shrimp siblings raised in ponds in Thailand and in raceways in Hawaii, shrimp growth can be improved after one generation of selection, even with a modest investment.

Authors examined whether beta-glucans extracted from bakers yeast could improve the survival and growth of Pacific white shrimp challenged with infectious myonecrosis virus.

In an NHP (necrotizing hepatopancreatitis) challenge test, shrimp from a Colombian breeding program had higher resistance and 30 percent greater survival than a control line of Taura syndrome virus-free shrimp.

Although concerns for the animal welfare of food animals are currently highest in the United Kingdom and European Union, they are also growing in other parts of the world.

In research on alternatives to formalin treatment to control Ich infestation, the authors performed a study that compared the immune responses of Nile tilapia and red tilapia against the parasite.

A study demonstrated that market-size shrimp can be profitably produced with zero water exchange in intensive raceways. The reuse of water that served for an earlier nursery study allowed the immediate establishment of a healthy microbial community in the grow-out study.
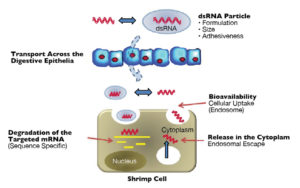
Therapeutics to harness an active RNA interference (RNAi) response in shrimp and protect against viral diseases could provide benefits to aquaculture.

As the demand for aquaculture products increases, so does the search for environmentally friendly alternatives to antibiotics. Alternatives to antibiotics include dietary prebiotics, probiotics and synbiotics.

In China, fleshy shrimp have had much higher market value than other shrimp species. China’s aquaculture scientists and fishery agencies have therefore worked closely with shrimp farmers to rebuild the farming industry for F. chinensis.

Although still being refined, the IMNV challenge method developed at the University of Arizona has shown promise as a tool to measure resistance in selected family lines of L. vannamei.

Although the application of selective breeding and genetics can yield dramatic results, the use of genetically improved stock varies widely among aquaculture sectors. Virtually all Atlantic salmon and rainbow trout producers use improved stock, while use of genetically improved tilapia varies widely.

Recirculating aquaculture systems have properties that can mature and stabilize the microbial community, creating a more benign bacterial flora in larval tanks.